Control System for the Quench Protection System¶
QPS controls in a nutshell¶
The Quench Protection System (QPS) is a CERN system deployed in the LHC and all accelerator testing facilities where superconducting elements can be found, as per its purpose: the protection of the superconducting elements against quenches.
The QPS is overall designed, developed and maintained in collaboration between three sections of the MPE group, TE-MPE-EP, TE-MPE-MP and ourselves, TE-MPE-CB. TE-MPE-EP and TE-MPE-MP are responsible for the field elements (hardware, electronics, firmware). Conversely, the TE-MPE-CB section is responsible for integrating these within the global CERN accelerator controls, and so for the software elements required for such integration. All three sections work closely together to integrate QPS hardware, firmware and software together, and then deploy, commission and support the operation of the whole system.
The QPS has an architecture similar to the standard SCADA stack, with 3 layers: - Field layer: composed by the QPS hardware devices. Performs read-out and real-time control, protecting the superconducting elements and extracting the energy accumulated in the superconducting magnets. - Control/data acquisition layer: manages a local group of devices, relays communications (commands, data) between the field and supervision layers, and the accelerator data management systems. - Supervision layer: user interfaces and programmable interfaces for high level interaction with the QPS. Includes LHC operational supervision, expert supervision, integration with synoptic software applications.
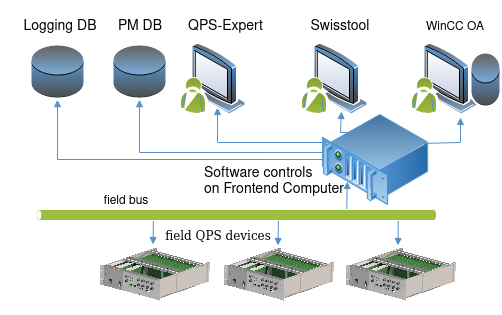
The 'controls' of the QPS actually encompasses everything from the communication with the field elements to the high-level UIs and APIs, i.e. the control/data acq. and supervision layers.
The QPS and its controls are distributed systems, their diverse elements scaling up to the LHC size; for instance: - >4000 field devices - ~100 field buses - ~50 control computers - ~100Mbps of continuous, aggregated data throughput for the LHC
Notably, the QPS controls leverage the common accelerator controls services and infrastructure, and integrates with several other LHC systems.
High Luminosity LHC¶
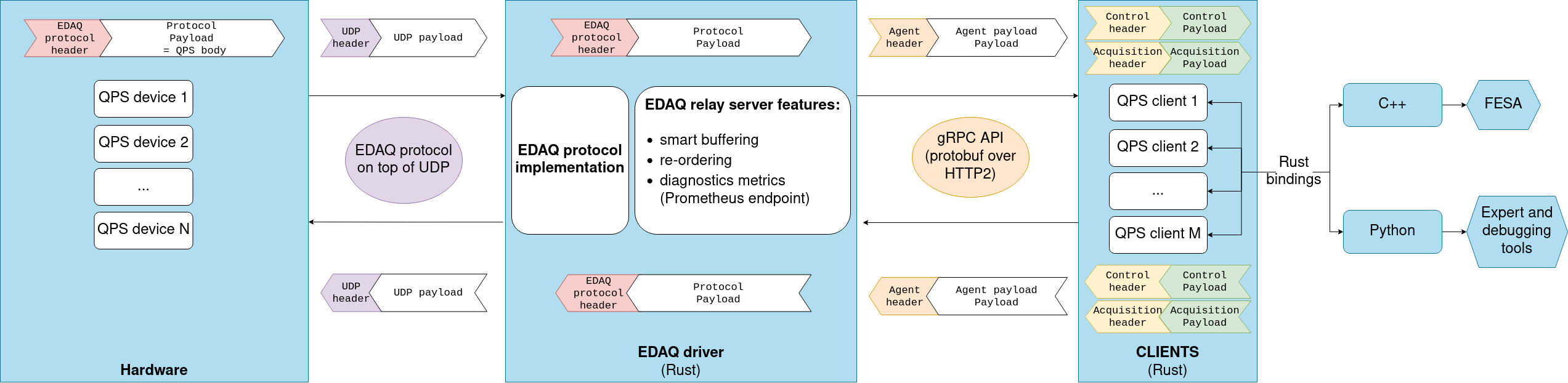
The QPS controls and data acquisition will be the stage of a technological upgrade in the context of the High Luminosity LHC (HL-LHC) project, where finer, more comprehensive measurements of the superconducting electrical circuits will be required, and so will a higher data throughput.
A new field bus and data acquisition solution was designed and developed to this
effect, based on the standard Ethernet technology. Named EDAQ, it entails
a communication protocol, its driver implementations and integration into CERN
accelerator controls and monitoring services.
Technologies¶
WorldFIPas fieldbus of the current QPS deployed in the LHCC++17, and the CERN in-houseFESAframework for the control applicationPython 3toolingJavafor the expert GUIsPrometheus,OpenSearch,Kibana,Grafanafor monitoring and tracingEthernet,UDP/IPfor the next generation 'EDAQ' fieldbus, for HL-LHCRust,gRPCandProtocol Buffersfor the EDAQ driver implementation
See also the list of publications and presentations on the topic.